Insulating the attic floor of a brick house with durable, waterproof closed-cell spray foam is an excellent choice for increasing...
Professional insulation of buildings with sprayed polyurethane foam
Professional insulation of buildings with sprayed polyurethane foam
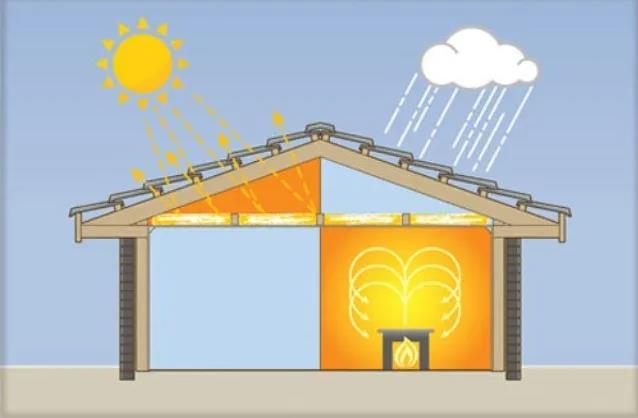
Spray foam insulation, like other types of insulation, saves energy costs and reduces utility bills. Buildings treated with foam insulation insulate 50% better than those with traditional insulation products. Properly applied insulation can be part of moisture protection, reducing the appearance of harmful mold and the likelihood of wood decay. In addition to regulating the temperature and humidity of the building, spray foam insulation is often used to reduce noise. Insulation prevents the spread of airborne sounds and reduces airborne sound transmission through the building’s roof, floor, and walls compared to an uninsulated structure. All types of insulation prevent energy loss. Some types, including spray foam, also seal air leakage. Insulation can save energy even in warm climates by reducing the need for air conditioning.
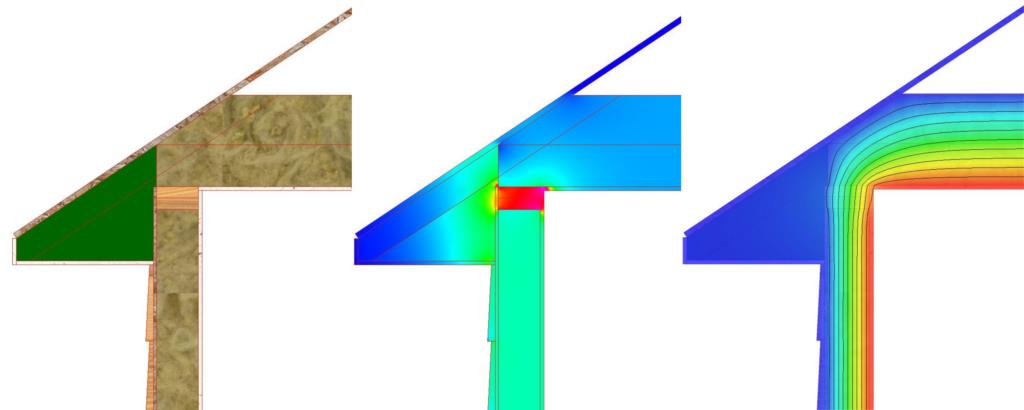
Adhered board insulating materials, over time, become thermal bridges as they compact and thus separate from each other and the underlying surface, creating larger gaps for air. In contrast, sprayed polyurethane foam adheres to the base surface, forming a continuous layer that insulates the surface without creating thermal bridges. If the base surface has any defects or cracks, the foam expands into those areas, bonding and sealing the surfaces, thus ensuring maximum effectiveness.

A significant advantage of flat roof insulation is that there is no need for a vapor barrier film, as the closed-cell polyurethane foam is inherently waterproof. With this technology, the application of bituminous sheets can also be avoided. In the case of external insulation, we apply UV-resistant protective paint to the closing surface, preventing sun radiation from causing damage to the insulation. Since there is no need to align boards with each other and fasten them to the surface with screws, glue, and various materials, there are no weak points in the insulated surface. Thanks to its flexibility, it excellently withstands damage from dilation movements. This solution can also eliminate previous leaks in the internal insulation of halls.

Due to the density of closed-cell polyurethane foam, it becomes an extremely hard material. With this technology, insulated surfaces can be functionally used even after the completion of the work. Not only can it serve as a previous storage space after insulating the attic floor, but even the concrete casting of the insulated surface can be realized upon demand, following the use of the material with the appropriate density.

Speaking of a well-established technology, with the appropriate equipment and expertise, the insulation of massive surfaces is possible on a daily basis. Following the cleaning of the surface to be insulated, the insulation material can be applied immediately, without any additional work processes such as cutting to size, gluing, or foil attachment. Thanks to this, we can undertake insulation projects for large surfaces with relatively short deadlines.
Insulating the attic floor of a brick house with durable, waterproof closed-cell spray foam is an excellent choice for increasing...
Insulating the ground floor of a lightweight structure house with closed-cell spray foam is an excellent method for efficient thermal...
Insulating closed-section joist cavities with closed-cell spray foam is an excellent choice for the efficient thermal insulation of buildings. Closed-cell...
Purfoam is a chemical product made up of two substances, isocyanate and polyol resin, which react when mixed with each other and expand to 30-60 times the volume of the liquid when sprayed into place. This expansion makes the blown mixture particularly useful, as it molds the shape of the surface to be insulated while providing a high thermal insulation value with virtually no air infiltration.
Otto Bayer is credited with the invention of polyurethane in 1937. He succeeded in synthesizing polyurethane foam by exploring his basic idea that dry foam materials could be created by mixing small amounts of chemicals. Polyurethane has been further developed for a variety of applications, from shoe soles and cushions to industrial uses. In the 1940s, rigid foam was used in airplanes, and in 1979, polyurethane began to be used to insulate buildings.
The heat resistance. The R-value is a term given to thermal resistance to heat flow. The higher the R-value of an insulation product, the more effective its insulating properties. Sprayed polyurethane foam is available in different densities and cell structures. Low-density foams are called open-cell foams, while higher-density foams are called closed-cell foams. Polyurethane foam has the highest R-value among insulation materials that can be used in homes and buildings. Polyurethane is a closed-cell foam insulation material that contains a low-conductivity gas in its cells. Due to the high thermal resistance of the gas, the initial R-value of sprayed polyurethane insulation is typically between R-3.4 and R-6.7 per inch. In comparison, glass wool typically has an R-value of only R-3 to R-4 per inch.
Spray polyurethane foam insulation can be classified into two different types: light density open cell spray foam insulation and medium density closed cell spray foam insulation. Both types of foam are thermosetting cellular plastic containing millions of small cells. Open cell insulation can be crushed in the hand and has a lower insulation value. The closed cell is stiff to the touch and all air cells are completely sealed. While closed-cell foam has a higher R-value, it is more expensive to purchase.
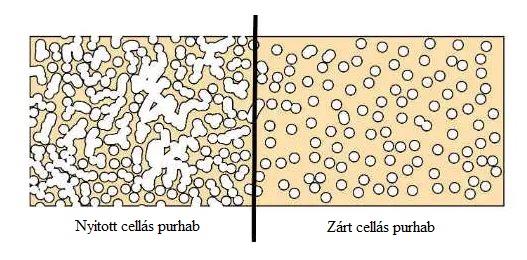

Medium-density closed-cell foam insulation is a rigid insulation material with a long-term thermal resistance R-value of 5.1 to 6 inches. If the required minimum thickness of 50 mm is built, this material is both a vapor barrier and an air barrier. The natural color of foam is usually yellow.
Light-density, open-cell foam insulation is a semi-rigid material with a spongy appearance that expands during installation to create small, open cells that are filled with carbon dioxide. Thanks to its ability to expand during the application process, it fills cracks, gaps and voids and forms an adhesive and airtight insulation for uneven surfaces or substrates. While the R value can vary, most open-cell purfoam products have an R value of about 3.8 per inch. Unlike medium-density closed-cell foam, the thinner layers of ocSPF are not very effective as a vapor barrier because air seeps through the open-cell structure. However, if it is built to a thickness of at least 140 mm, it already works as an air barrier. It is often used for interior walls because it provides sound reduction by blocking and absorbing air leakage. Generally recommended for indoor use only.